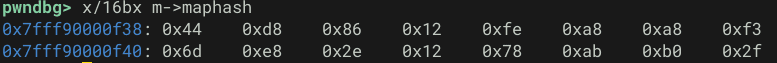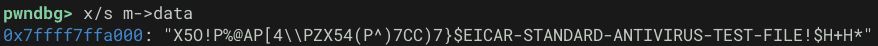特に目的なく ClamAV のコードを読み進めているのですが、一区切りついたのでとりあえず ClamAV で Eicar ファイルのスキャンを行った際に検出されるまでの一連の動作に関するメモを公開することにしました。
もくじ
clamscan もしくは clamdscan によるファイルのスキャン
clamdscan はシステムで稼働中の clamd のクライアントとしてファイルスキャンを行うことができるクライアントプログラムです。
一方で、clamscan は ClamAV の libclamav を使用してファイルやディレクトリに対する Scanner として動作するプログラムです。
clamdscan とは異なり、clamscan を使用する場合は実行中の clamd インスタンスを必要とせず、呼び出し時に新しくスキャンエンジンを作成し、 virus database のロードを行います。
参考:Scanning - ClamAV Documentation
まずは実際に clamscan と clamdscan によるスキャンを試してみます。
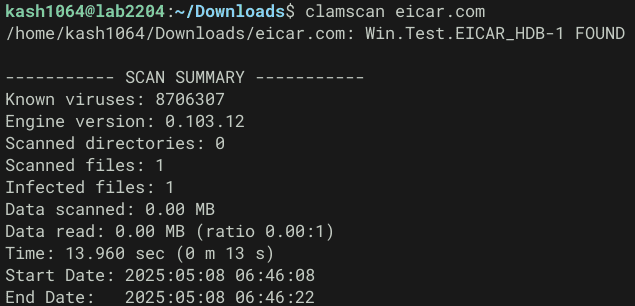
以下のコマンドで取得した Eicar テストファイルを検出できました。
# Eicar ファイルの取得
wget https://secure.eicar.org/eicar.com
# 検出テスト
clamscan eicar.com
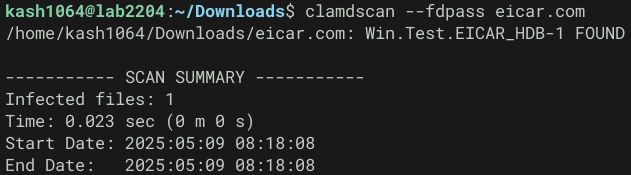
clamdscan --fdpass eicar.comなお、clamd を clamav ユーザーで実行する設定の場合、clamdscan でスキャン要求したファイルに clamd がアクセスできず、File path check failure: Permission denied. ERROR によりスキャンに失敗するようです。
そのため、今回は clamd を LocalSocket モードで起動した上で、ファイルディスクリプタを clamd にパスするオプションである --fdpass を使用してスキャン要求を実行しています。
参考:Configure clamdscan to scan all files on a system on Ubuntu 12.04 - Stack Overflow
clamscan の各種オプション
clamscan の場合、clamdscan と比較してかなり多くのオプションを使用することができます。
以下は、バージョン 0.104.0 の Help テキストです。
$ clamscan --help
Clam AntiVirus: Scanner 0.104.0
By The ClamAV Team: https://www.clamav.net/about.html#credits
(C) 2021 Cisco Systems, Inc.
clamscan [options] [file/directory/-]
--help -h Show this help
--version -V Print version number
--verbose -v Be verbose
--archive-verbose -a Show filenames inside scanned archives
--debug Enable libclamav's debug messages
--quiet Only output error messages
--stdout Write to stdout instead of stderr. Does not affect 'debug' messages.
--no-summary Disable summary at end of scanning
--infected -i Only print infected files
--suppress-ok-results -o Skip printing OK files
--bell Sound bell on virus detection
--tempdir=DIRECTORY Create temporary files in DIRECTORY
--leave-temps[=yes/no(*)] Do not remove temporary files
--gen-json[=yes/no(*)] Generate JSON metadata for the scanned file(s). For testing & development use ONLY.
JSON will be printed if --debug is enabled.
A JSON file will dropped to the temp directory if --leave-temps is enabled.
--database=FILE/DIR -d FILE/DIR Load virus database from FILE or load all supported db files from DIR
--official-db-only[=yes/no(*)] Only load official signatures
--log=FILE -l FILE Save scan report to FILE
--recursive[=yes/no(*)] -r Scan subdirectories recursively
--allmatch[=yes/no(*)] -z Continue scanning within file after finding a match
--cross-fs[=yes(*)/no] Scan files and directories on other filesystems
--follow-dir-symlinks[=0/1(*)/2] Follow directory symlinks (0 = never, 1 = direct, 2 = always)
--follow-file-symlinks[=0/1(*)/2] Follow file symlinks (0 = never, 1 = direct, 2 = always)
--file-list=FILE -f FILE Scan files from FILE
--remove[=yes/no(*)] Remove infected files. Be careful!
--move=DIRECTORY Move infected files into DIRECTORY
--copy=DIRECTORY Copy infected files into DIRECTORY
--exclude=REGEX Don't scan file names matching REGEX
--exclude-dir=REGEX Don't scan directories matching REGEX
--include=REGEX Only scan file names matching REGEX
--include-dir=REGEX Only scan directories matching REGEX
--bytecode[=yes(*)/no] Load bytecode from the database
--bytecode-unsigned[=yes/no(*)] Load unsigned bytecode
**Caution**: You should NEVER run bytecode signatures from untrusted sources.
Doing so may result in arbitrary code execution.
--bytecode-timeout=N Set bytecode timeout (in milliseconds)
--statistics[=none(*)/bytecode/pcre] Collect and print execution statistics
--detect-pua[=yes/no(*)] Detect Possibly Unwanted Applications
--exclude-pua=CAT Skip PUA sigs of category CAT
--include-pua=CAT Load PUA sigs of category CAT
--detect-structured[=yes/no(*)] Detect structured data (SSN, Credit Card)
--structured-ssn-format=X SSN format (0=normal,1=stripped,2=both)
--structured-ssn-count=N Min SSN count to generate a detect
--structured-cc-count=N Min CC count to generate a detect
--structured-cc-mode=X CC mode (0=credit debit and private label, 1=credit cards only
--scan-mail[=yes(*)/no] Scan mail files
--phishing-sigs[=yes(*)/no] Enable email signature-based phishing detection
--phishing-scan-urls[=yes(*)/no] Enable URL signature-based phishing detection
--heuristic-alerts[=yes(*)/no] Heuristic alerts
--heuristic-scan-precedence[=yes/no(*)] Stop scanning as soon as a heuristic match is found
--normalize[=yes(*)/no] Normalize html, script, and text files. Use normalize=no for yara compatibility
--scan-pe[=yes(*)/no] Scan PE files
--scan-elf[=yes(*)/no] Scan ELF files
--scan-ole2[=yes(*)/no] Scan OLE2 containers
--scan-pdf[=yes(*)/no] Scan PDF files
--scan-swf[=yes(*)/no] Scan SWF files
--scan-html[=yes(*)/no] Scan HTML files
--scan-xmldocs[=yes(*)/no] Scan xml-based document files
--scan-hwp3[=yes(*)/no] Scan HWP3 files
--scan-archive[=yes(*)/no] Scan archive files (supported by libclamav)
--alert-broken[=yes/no(*)] Alert on broken executable files (PE & ELF)
--alert-broken-media[=yes/no(*)] Alert on broken graphics files (JPEG, TIFF, PNG, GIF)
--alert-encrypted[=yes/no(*)] Alert on encrypted archives and documents
--alert-encrypted-archive[=yes/no(*)] Alert on encrypted archives
--alert-encrypted-doc[=yes/no(*)] Alert on encrypted documents
--alert-macros[=yes/no(*)] Alert on OLE2 files containing VBA macros
--alert-exceeds-max[=yes/no(*)] Alert on files that exceed max file size, max scan size, or max recursion limit
--alert-phishing-ssl[=yes/no(*)] Alert on emails containing SSL mismatches in URLs
--alert-phishing-cloak[=yes/no(*)] Alert on emails containing cloaked URLs
--alert-partition-intersection[=yes/no(*)] Alert on raw DMG image files containing partition intersections
--nocerts Disable authenticode certificate chain verification in PE files
--dumpcerts Dump authenticode certificate chain in PE files
--max-scantime=#n Scan time longer than this will be skipped and assumed clean (milliseconds)
--max-filesize=#n Files larger than this will be skipped and assumed clean
--max-scansize=#n The maximum amount of data to scan for each container file (**)
--max-files=#n The maximum number of files to scan for each container file (**)
--max-recursion=#n Maximum archive recursion level for container file (**)
--max-dir-recursion=#n Maximum directory recursion level
--max-embeddedpe=#n Maximum size file to check for embedded PE
--max-htmlnormalize=#n Maximum size of HTML file to normalize
--max-htmlnotags=#n Maximum size of normalized HTML file to scan
--max-scriptnormalize=#n Maximum size of script file to normalize
--max-ziptypercg=#n Maximum size zip to type reanalyze
--max-partitions=#n Maximum number of partitions in disk image to be scanned
--max-iconspe=#n Maximum number of icons in PE file to be scanned
--max-rechwp3=#n Maximum recursive calls to HWP3 parsing function
--pcre-match-limit=#n Maximum calls to the PCRE match function.
--pcre-recmatch-limit=#n Maximum recursive calls to the PCRE match function.
--pcre-max-filesize=#n Maximum size file to perform PCRE subsig matching.
--disable-cache Disable caching and cache checks for hash sums of scanned files.
Pass in - as the filename for stdin.
(*) Default scan settings
(**) Certain files (e.g. documents, archives, etc.) may in turn contain other
files inside. The above options ensure safe processing of this kind of data.clamscan では、--quiet や --infected、--no-summary のようにスキャン結果などの出力をコントロールできるオプションや、スキャンに使用するエンジンでロードする virus database の指定や検出されたファイルの削除や隔離などを指定するオプションなどがあります。
また、他にもスキャン対象や除外の条件などを細かく指定するオプションが数多く存在しています。
clamdscan のオプション
clamdscan はシステムで稼働中の clamd のクライアントとしてファイルスキャンを行うため、実行時に毎回エンジンと virus database をロードする clamscan とは異なり、実行時に選択できるスキャンオプションがかなり少ない代わりに、すでに実行中の clamd によるスキャンを行うため、スキャンのオーバーヘッドが小さくなるメリットがあります。
$ clamdscan --help
Clam AntiVirus: Daemon Client 0.104.0
By The ClamAV Team: https://www.clamav.net/about.html#credits
(C) 2021 Cisco Systems, Inc.
clamdscan [options] [file/directory/-]
--help -h Show this help
--version -V Print version number and exit
--verbose -v Be verbose
--quiet Be quiet, only output error messages
--stdout Write to stdout instead of stderr. Does not affect 'debug' messages.
(this help is always written to stdout)
--log=FILE -l FILE Save scan report in FILE
--file-list=FILE -f FILE Scan files from FILE
--ping -p A[:I] Ping clamd up to [A] times at optional interval [I] until it responds.
--wait -w Wait up to 30 seconds for clamd to start. Optionally use alongside --ping to set attempts [A] and interval [I] to check clamd.
--remove Remove infected files. Be careful!
--move=DIRECTORY Move infected files into DIRECTORY
--copy=DIRECTORY Copy infected files into DIRECTORY
--config-file=FILE Read configuration from FILE.
--allmatch -z Continue scanning within file after finding a match.
--multiscan -m Force MULTISCAN mode
--infected -i Only print infected files
--no-summary Disable summary at end of scanning
--reload Request clamd to reload virus database
--fdpass Pass filedescriptor to clamd (useful if clamd is running as a different user)
--stream Force streaming files to clamd (for debugging and unit testing)clamdscan でスキャンを行う場合にも、clamscan と同様に --quiet や --infected、--no-summary オプションなどによる表示の制御はある程度行うことができます。
また、--remove や --move などによる検出ファイルの削除/隔離についても同様に行うことができます。
clamdscan によるスキャン動作
今回はまず、clamdscan によりスキャンを行う際の動作を追跡してみることにします。
clamdscan の main 関数では、実行時オプションを一通りパースした後、以下のコードを実行するようです。
date_start = time(NULL);
gettimeofday(&t1, NULL);
ret = client(opts, &infected, &err);
optfree(clamdopts);
/* TODO: Implement STATUS in clamd */
if (!optget(opts, "no-summary")->enabled) {
struct tm tmp;
date_end = time(NULL);
gettimeofday(&t2, NULL);
ds = t2.tv_sec - t1.tv_sec;
dms = t2.tv_usec - t1.tv_usec;
ds -= (dms < 0) ? (1) : (0);
dms += (dms < 0) ? (1000000) : (0);
logg("\n----------- SCAN SUMMARY -----------\n");
logg("Infected files: %d\n", infected);
if (err)
logg("Total errors: %d\n", err);
if (notremoved) {
logg("Not removed: %d\n", notremoved);
}
if (notmoved) {
logg("Not moved: %d\n", notmoved);
}
logg("Time: %d.%3.3d sec (%d m %d s)\n", ds, dms / 1000, ds / 60, ds % 60);
#ifdef _WIN32
if (0 != localtime_s(&tmp, &date_start)) {
#else
if (!localtime_r(&date_start, &tmp)) {
#endif
logg("!Failed to get local time for Start Date.\n");
}
strftime(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%Y:%m:%d %H:%M:%S", &tmp);
logg("Start Date: %s\n", buffer);
#ifdef _WIN32
if (0 != localtime_s(&tmp, &date_end)) {
#else
if (!localtime_r(&date_end, &tmp)) {
#endif
logg("!Failed to get local time for End Date.\n");
}
strftime(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%Y:%m:%d %H:%M:%S", &tmp);
logg("End Date: %s\n", buffer);
}参考:clamav/clamdscan/clamdscan.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
client 関数の実行
初めに、パースしたオプションを含むリストへのポインタを含む変数を引数として client 関数を呼び出します。
client 関数では const struct optstruct *opts で受け取ったリストから各オプションなどの設定を取り出し、対象ファイルのスキャンを行った結果を返します。
struct optstruct {
char *name;
char *cmd;
char *strarg;
long long numarg;
int enabled;
int active;
int flags;
int idx;
struct optstruct *nextarg;
struct optstruct *next;
char **filename; /* cmdline */
};
int ds, dms, ret, infected = 0, err = 0;
struct optstruct *opts;
ret = client(opts, &infected, &err);この client 関数は clamdscan/client.c の中で以下の通り実装されています。
int client(const struct optstruct *opts, int *infected, int *err)
{
int remote, scantype, session = 0, errors = 0, scandash = 0, maxrec, flags = 0;
const char *fname;
if (optget(opts, "wait")->enabled) {
int16_t ping_result = ping_clamd(opts);
switch (ping_result) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
return (int)CL_ETIMEOUT;
default:
return (int)CL_ERROR;
}
}
scandash = (opts->filename && opts->filename[0] && !strcmp(opts->filename[0], "-") && !optget(opts, "file-list")->enabled && !opts->filename[1]);
remote = isremote(opts) | optget(opts, "stream")->enabled;
#ifdef HAVE_FD_PASSING
if (!remote && optget(clamdopts, "LocalSocket")->enabled && (optget(opts, "fdpass")->enabled || scandash)) {
scantype = FILDES;
session = optget(opts, "multiscan")->enabled;
} else
#endif
if (remote || scandash) {
scantype = STREAM;
session = optget(opts, "multiscan")->enabled;
} else if (optget(opts, "multiscan")->enabled)
scantype = MULTI;
else if (optget(opts, "allmatch")->enabled)
scantype = ALLMATCH;
else
scantype = CONT;
maxrec = optget(clamdopts, "MaxDirectoryRecursion")->numarg;
maxstream = optget(clamdopts, "StreamMaxLength")->numarg;
if (optget(clamdopts, "FollowDirectorySymlinks")->enabled)
flags |= CLI_FTW_FOLLOW_DIR_SYMLINK;
if (optget(clamdopts, "FollowFileSymlinks")->enabled)
flags |= CLI_FTW_FOLLOW_FILE_SYMLINK;
flags |= CLI_FTW_TRIM_SLASHES;
*infected = 0;
if (scandash) {
int sockd, ret;
STATBUF sb;
if (FSTAT(0, &sb) < 0) {
logg("client.c: fstat failed for file name \"%s\", with %s\n.",
opts->filename[0], strerror(errno));
return 2;
}
if ((sb.st_mode & S_IFMT) != S_IFREG) scantype = STREAM;
if ((sockd = dconnect()) >= 0 && (ret = dsresult(sockd, scantype, NULL, &ret, NULL)) >= 0)
*infected = ret;
else
errors = 1;
if (sockd >= 0) closesocket(sockd);
} else if (opts->filename || optget(opts, "file-list")->enabled) {
if (opts->filename && optget(opts, "file-list")->enabled)
logg("^Only scanning files from --file-list (files passed at cmdline are ignored)\n");
while ((fname = filelist(opts, NULL))) {
if (!strcmp(fname, "-")) {
logg("!Scanning from standard input requires \"-\" to be the only file argument\n");
continue;
}
errors += client_scan(fname, scantype, infected, err, maxrec, session, flags);
/* this may be too strict
if(errors >= 10) {
logg("!Too many errors\n");
break;
}
*/
}
} else {
errors = client_scan("", scantype, infected, err, maxrec, session, flags);
}
return *infected ? 1 : (errors ? 2 : 0);
}参考:clamav/clamdscan/client.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
scantype の設定
この関数内では最初に scandash と remote の 2 つの変数を宣言します。
scandash = (opts->filename && opts->filename[0] && !strcmp(opts->filename[0], "-") && !optget(opts, "file-list")->enabled && !opts->filename[1]);
remote = isremote(opts) | optget(opts, "stream")->enabled;scandash は、引数として受け取った opts について、(opts->filename && opts->filename[0] && !strcmp(opts->filename[0], "-") と !optget(opts, "file-list")->enabled && !opts->filename[1]) の AND を格納しています。
これは、file-list オプションが無効でかつ入力が - を使用するものである場合のチェックを行うためのもののようです。
参考:linux - What’s the magic of ”-” (a dash) in command-line parameters? - Stack Overflow
また、remote = isremote(opts) | optget(opts, "stream")->enabled; は、clamdscan がリモート実行されているか、もしくは Stream オプションが有効化されているか否かをチェックしています。
この scandash か remote のフラグが真である場合には scantype が STREAM となるようです。
しかし、今回は LocalSocket を使用し、かつ fdpass オプションを有効化してスキャン要求を行っており、scantype は FILDES となるためこの行は無視します。
#ifdef HAVE_FD_PASSING
if (!remote && optget(clamdopts, "LocalSocket")->enabled && (optget(opts, "fdpass")->enabled || scandash)) {
scantype = FILDES;
session = optget(opts, "multiscan")->enabled;
} else
#endif
if (remote || scandash) {
scantype = STREAM;
session = optget(opts, "multiscan")->enabled;
} else if (optget(opts, "multiscan")->enabled)
scantype = MULTI;
else if (optget(opts, "allmatch")->enabled)
scantype = ALLMATCH;
else
scantype = CONT;スキャン関数の呼び出し
今回のように scandash のフラグが False である場合、scantype などの変数を引数としてそのまま client_scan 関数が実行されます。
*infected = 0;
if (scandash) {
/* 省略 */
} else {
errors = client_scan("", scantype, infected, err, maxrec, session, flags);
}この中では、file として与えられるスキャン対象のファイルの絶対パスの取得が行われます。
また、受け取った session の値(session = optget(opts, "multiscan")->enabled;) によって、さらに serialclientscan 関数もしくは parallelclientscan 関数を呼び出します。
/* Recursively scans a path with the given scantype
* Returns non zero for serious errors, zero otherwise */
static int client_scan(const char *file, int scantype, int *infected, int *err, int maxlevel, int session, int flags)
{
int ret;
char *real_path = NULL;
char *fullpath = NULL;
/* Convert relative path to fullpath */
fullpath = makeabs(file);
/* Convert fullpath to the real path (evaluating symlinks and . and ..).
Doing this early on will ensure that the scan results will appear consistent
across regular scans, --fdpass scans, and --stream scans. */
if (CL_SUCCESS != cli_realpath(fullpath, &real_path)) {
logg("*client_scan: Failed to determine real filename of %s.\n", fullpath);
} else {
free(fullpath);
fullpath = real_path;
}
if (!fullpath)
return 0;
if (!session)
ret = serial_client_scan(fullpath, scantype, infected, err, maxlevel, flags);
else
ret = parallel_client_scan(fullpath, scantype, infected, err, maxlevel, flags);
free(fullpath);
return ret;
}今回のように multiscan オプションを使用しない場合、serialclientscan 関数にファイルや scantype などの情報が渡されます。
/* Non-IDSESSION handler
* Returns non zero for serious errors, zero otherwise */
int serial_client_scan(char *file, int scantype, int *infected, int *err, int maxlevel, int flags)
{
struct cli_ftw_cbdata data;
struct client_serial_data cdata;
int ftw;
cdata.infected = 0;
cdata.files = 0;
cdata.errors = 0;
cdata.printok = printinfected ^ 1;
cdata.scantype = scantype;
data.data = &cdata;
ftw = cli_ftw(file, flags, maxlevel ? maxlevel : INT_MAX, serial_callback, &data, ftw_chkpath);
*infected += cdata.infected;
*err += cdata.errors;
if (!cdata.errors && (ftw == CL_SUCCESS || ftw == CL_BREAK)) {
if (cdata.printok)
logg("~%s: OK\n", file);
return 0;
} else if (!cdata.files) {
logg("~%s: No files scanned\n", file);
return 0;
}
return 1;
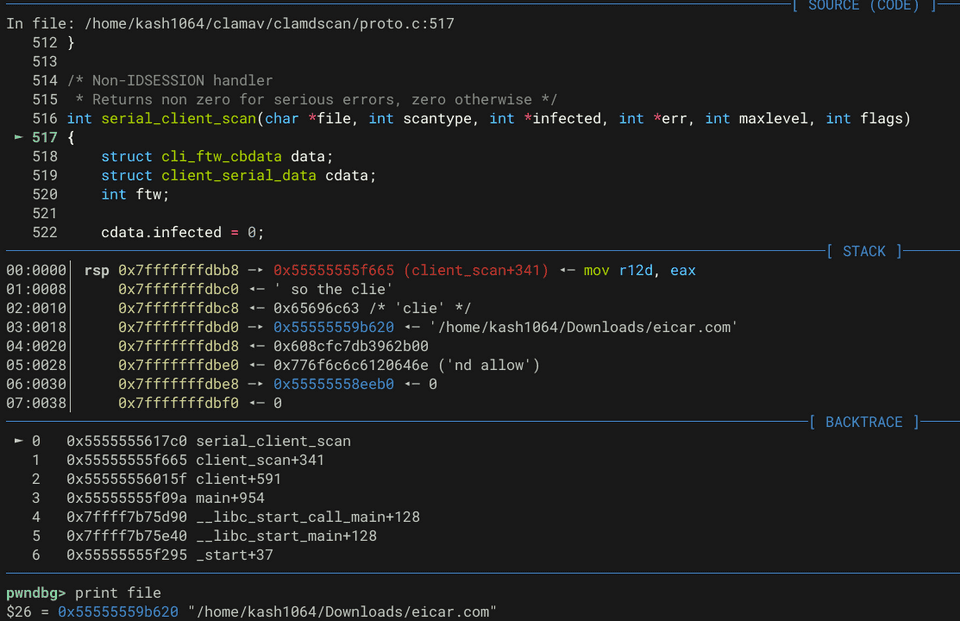
}この時、char *file にはスキャン対象のファイルの完全パスが保存されていることをデバッガで確認できます。
この関数の中では、clientserialdata 構造体の変数 cdata を初期化し、それを cliftwcbdata 構造体の変数 data の data メンバに保存した上で、ファイルなどの情報と共に cli_ftw 関数を呼び出しています。
/* wrap void*, so that we don't mix it with some other pointer */
struct cli_ftw_cbdata {
void *data;
};
/* Used by serial_callback() */
struct client_serial_data {
int infected;
int scantype;
int printok;
int files;
int errors;
};
struct cli_ftw_cbdata data;
struct client_serial_data cdata;
int ftw;
cdata.infected = 0;
cdata.files = 0;
cdata.errors = 0;
cdata.printok = printinfected ^ 1;
cdata.scantype = scantype;
data.data = &cdata;
ftw = cli_ftw(file, flags, maxlevel ? maxlevel : INT_MAX, serial_callback, &data, ftw_chkpath);
*infected += cdata.infected;
*err += cdata.errors;cli_ftw 関数の実行
cliftw 関数は libclamav の otherscommon.c 内で実装されている関数で、大きく以下の操作を行うようです。
- handlefiletype 関数によるファイルタイプの取得とスキップ対象か否かのチェック(ファイルタイプが `ftskippedlink
かftskipped_special` の場合にはスキップ処理が行われるっぽい) - ftskipped 関数によるスキップ有無のチェック(`ft != ftregular && ft != ft_directory` が True になるとスキップされるっぽい)
- 対象がディレクトリの場合は直接、ファイルの場合には handleentry 関数を経由して、コールバック関数(serialclientscan 関数から実行している場合は serialcallback 関数) が実行されます。
参考:clamav/libclamav/others_common.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
以上の通り、ファイルを指定して clamdscan を実行した場合、direntdata 構造体の変数 entry の filename メンバにスキャン対象のファイルのフルパスを格納した上で、handleentry 関数の呼び出しが行われます。
/*
* Now call handle_entry() to either call the callback for files,
* or recurse deeper into the file tree walk.
* TODO: Recursion is bad, this whole thing should be iterative
*/
if (entry.is_dir) {
entry.dirname = path;
} else {
/* Allocate the filename for the callback function within the handle_entry function. TODO: this FTW code is spaghetti, refactor. */
filename_for_handleentry = cli_strdup(path);
if (NULL == filename_for_handleentry) {
goto done;
}
entry.filename = filename_for_handleentry;
}
status = handle_entry(&entry, flags, maxdepth, callback, data, pathchk);実際に handle_entry の呼び出しをデバッグしてみると、filename メンバに eicar.com の完全パスが保存されていることを確認できます。
> print *(struct dirent_data *)entry
$3 = {
filename = 0x55555559b0c0 "/home/kash1064/Downloads/eicar.com",
dirname = 0x0,
statbuf = <optimized out>,
ino = <optimized out>,
is_dir = <optimized out>
}この handleentry 関数は、単に callback 関数(今回の場合は serialcallback 関数)を呼び出すだけの機能を持ちます。
第 4 引数の cliftwreason には visit_file が渡されます。
static int handle_entry(struct dirent_data *entry, int flags, int maxdepth, cli_ftw_cb callback, struct cli_ftw_cbdata *data, cli_ftw_pathchk pathchk)
{
if (!entry->is_dir) {
return callback(entry->statbuf, entry->filename, entry->filename, visit_file, data);
} else {
return cli_ftw_dir(entry->dirname, flags, maxdepth, callback, data, pathchk);
}
}serial_callback の呼び出し
serialcallback 関数は clamdscan/proto.c で実装されており、serialclientscan 関数で cliftw を呼び出した際のコールバック関数として渡された関数です。
参考:clamav/clamdscan/proto.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
この中ではいくつかのチェックを行った後、dconnect 関数で clamd デーモンに接続し、取得したソケット経由で dsresult 関数によるスキャン要求を行います。
dsresult 関数は検出されたファイル(infected files) の数を整数値で返します。
if ((sockd = dconnect()) < 0) {
c->errors++;
goto done;
}
ret = dsresult(sockd, c->scantype, f, &c->printok, &c->errors);
closesocket(sockd);
if (ret < 0) {
c->errors++;
goto done;
}
c->infected += ret;
if (reason == visit_directory_toplev) {
status = CL_BREAK;
goto done;
}dsresult 関数の呼び出しをデバッグしてみると、第 1 引数の sockd に 3、第 3 引数の filename にスキャン対象のファイルパスが格納されていることを確認できます。
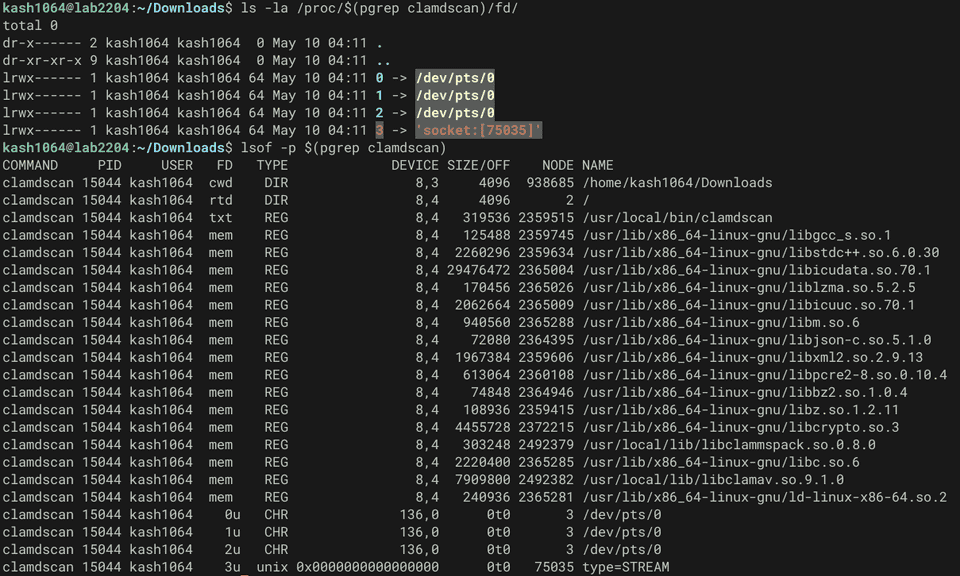
sockd は dconnect 関数内で(LocalSocket モードの場合には) sockd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) により取得したソケットのファイルディスクリプタです。
実際、ls -la /proc/$(pgrep clamdscan)/fd/ や lsof -p $(pgrep clamdscan) コマンドで clamdscan がこのファイルディスクリプタを使用したソケットを開いていることを確認できます。
dsresult 関数では、いくつかの構造体変数などの初期化を行った後、scantype の値に応じて clamd への要求を行います。
今回は fdpass オプションを使用した上で scantype は FILDES となっているため、まずは len = send_fdpass(sockd, filename); が呼び出されます。
switch (scantype) {
case MULTI:
case CONT:
case ALLMATCH:
/* 省略 */
case STREAM:
/* 省略 */
#ifdef HAVE_FD_PASSING
case FILDES:
/* NULL filename safe in send_fdpass() */
len = send_fdpass(sockd, filename);
break;
#endif
}sendfdpass 関数では、`fd = open(filename, ORDONLY)` で取得したスキャンファイルのファイルディスクリプタを含む情報を sendmsg システムコールで clamd に送信しています。
iov[0].iov_base = dummy;
iov[0].iov_len = 1;
memset(&msg, 0, sizeof(msg));
msg.msg_control = fdbuf;
msg.msg_iov = iov;
msg.msg_iovlen = 1;
msg.msg_controllen = CMSG_LEN(sizeof(int));
cmsg = CMSG_FIRSTHDR(&msg);
cmsg->cmsg_len = CMSG_LEN(sizeof(int));
cmsg->cmsg_level = SOL_SOCKET;
cmsg->cmsg_type = SCM_RIGHTS;
*(int *)CMSG_DATA(cmsg) = fd;
if (sendmsg(sockd, &msg, 0) == -1) {
logg("!FD send failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
close(fd);
return -1;
}clamd のデバッグ
まず、ClamAV をソースコードからビルドして OnAccessScan をセットアップするまでのまとめ の手順で以下のコマンドを使用し、clamd を含む ClamAV のコンポーネントを Debug ビルドとしてコンパイルします。
cmake .. \
-D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug \
-D OPTIMIZE=OFF \
-D ENABLE_EXAMPLES=OFF \
-D ENABLE_STATIC_LIB=ON \
-D ENABLE_SYSTEMD=ON
cmake --build . --target installこれで clamd を実行して gdb -p $(pgrep clamd) でデバッグすると、clamdscan によるスキャン実行時に以下のデバッグ出力を得ることができます。
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Got new connection, FD 12
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Received POLLIN|POLLHUP on fd 6
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $fds_poll_recv: timeout after 30 seconds
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Received POLLIN|POLLHUP on fd 12
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Receveived a file descriptor: 13
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $got command FILDES (7, 9), argument:
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $RECVTH: FILDES command complete
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $mode -> MODE_WAITREPLY
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Breaking command loop, mode is no longer MODE_COMMAND
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Consumed entire command
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Number of file descriptors polled: 1 fds
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $fds_poll_recv: timeout after 600 seconds
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $THRMGR: queue (single) crossed low threshold -> signaling
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $THRMGR: queue (bulk) crossed low threshold -> signaling
LibClamAV debug: cli_get_filepath_from_filedesc: File path for fd [13] is: /home/kash1064/Downloads/eicar.com
LibClamAV debug: Recognized ASCII text
LibClamAV debug: cache_check: 44d88612fea8a8f36de82e1278abb02f is negative
LibClamAV debug: matcher_run: performing regex matching on full map: 0+68(68) >= 68
LibClamAV debug: FP SIGNATURE: 44d88612fea8a8f36de82e1278abb02f:68:Win.Test.EICAR_HDB-1
LibClamAV debug: hashtab: Freeing hashset, elements: 0, capacity: 0
LibClamAV debug: Win.Test.EICAR_HDB-1 found
LibClamAV debug: cli_magic_scan_desc: returning 1 at line 4605
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> /home/kash1064/Downloads/eicar.com: Win.Test.EICAR_HDB-1(44d88612fea8a8f36de82e1278abb02f:68) FOUND
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Closed fd 13
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Finished scanthread
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $Scanthread: connection shut down (FD 12)
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $THRMGR: queue (single) crossed low threshold -> signaling
Sat May 10 06:59:27 2025 -> $THRMGR: queue (bulk) crossed low threshold -> signalingここから、clamd の scanner.c で実装されている cligetfilepathfromfiledesc 関数などが呼び出されていることがわかります。
参考:clamav/clamd/scanner.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
clamd 側でファイルパスを取得する
この時呼び出される cligetfilepathfromfiledesc 関数では、受け取ったファイルディスクリプタから readlink システムコールを使用して取得したスキャン対象のファイルのフルパスを fname に保存します。
char fname[PATH_MAX];
char link[32];
memset(&fname, 0, PATH_MAX);
snprintf(link, sizeof(link), "/proc/self/fd/%u", desc);
link[sizeof(link) - 1] = '\0';
if (-1 == (linksz = readlink(link, fname, PATH_MAX - 1))) {
cli_dbgmsg("cli_get_filepath_from_filedesc: Failed to resolve filename for descriptor %d (%s)\n", desc, link);
status = CL_EOPEN;
goto done;
}さらに、取得したファイルパスを evaluated_filepath として保存した後に、関数呼び出し時に引数として受け取った filepath に代入しています。
cli_dbgmsg("cli_get_filepath_from_filedesc: File path for fd [%d] is: %s\n", desc, evaluated_filepath);
status = CL_SUCCESS;
*filepath = evaluated_filepath;この関数の終了をデバッガで追跡すると、scanner.c の scanfd 関数から呼び出されていました。
/* Try and get the real filename, for logging purposes */
if (!stream) {
if (CL_SUCCESS != cli_get_filepath_from_filedesc(fd, &filepath)) {
logg("*%s: Unable to determine the filepath given the file descriptor.\n", fdstr);
} else {
log_filename = filepath;
}
}参考:clamav/clamd/scanner.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
スキャンコールバック関数の実行
ここでファイルディスクリプタから取得したファイルパスは、logfilename として保存された後 clscandesc_callback 関数に渡されます。
thrmgr_setactivetask(fdstr, NULL);
context.filename = fdstr;
context.virsize = 0;
context.scandata = NULL;
ret = cl_scandesc_callback(fd, log_filename, &virname, scanned, engine, options, &context);
thrmgr_setactivetask(NULL, NULL);
if (thrmgr_group_need_terminate(conn->group)) {
logg("*Client disconnected while scanjob was active\n");
ret = ret == CL_ETIMEOUT ? ret : CL_BREAK;
goto done;
}上記のコードでは、clscandesccallback 関数の呼び出し前に thrmgr_setactivetask 関数による fdstr の登録と context の初期化が行われています。
その後、clscandesccallback 関数にファイルディスクリプタやファイルパスを渡し、スキャンを行います。
/**
* @brief Scan a file, given a file descriptor.
*
* This callback variant allows the caller to provide a context structure that caller provided callback functions can interpret.
*
* @param desc File descriptor of an open file. The caller must provide this or the map.
* @param filename (optional) Filepath of the open file descriptor or file map.
* @param[out] virname Will be set to a statically allocated (i.e. needs not be freed) signature name if the scan matches against a signature.
* @param[out] scanned The number of bytes scanned.
* @param engine The scanning engine.
* @param scanoptions Scanning options.
* @param[in,out] context An opaque context structure allowing the caller to record details about the sample being scanned.
* @return cl_error_t CL_CLEAN, CL_VIRUS, or an error code if an error occured during the scan.
*/
extern cl_error_t cl_scandesc_callback(int desc, const char *filename, const char **virname, unsigned long int *scanned, const struct cl_engine *engine, struct cl_scan_options *scanoptions, void *context);この clscandesccallback 関数は libclamav の scanner.c で実装されています。
このコード内では、受け取ったファイルパスから clibasename 関数でファイル名を filenamebase として取り出し、fmap 関数にて ClamAV によるファイルスキャンを行うために使用される fmap_t 構造体としてマッピングします。
if (NULL != filename) {
(void)cli_basename(filename, strlen(filename), &filename_base);
}
if (NULL == (map = fmap(desc, 0, sb.st_size, filename_base))) {
cli_errmsg("CRITICAL: fmap() failed\n");
status = CL_EMEM;
goto done;
}
status = scan_common(map, filename, virname, scanned, engine, scanoptions, context);参考:clamav/libclamav/scanners.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
マッピングされた構造体は、ファイルパスやその他の情報と共に scan_common 関数に渡され、この中で実際のウイルススキャンが行われます。
fmap_t 構造体について
ClamAV では clfmapt(fmap_t) というデータ構造でファイルを効率的にスキャンするためのメモリマッピングを行います。
struct cl_fmap;
typedef cl_fmap_t fmap_t;
struct cl_fmap {
/* handle interface */
void *handle;
clcb_pread pread_cb;
/* internal */
time_t mtime;
uint64_t pages;
uint64_t pgsz;
uint64_t paged;
uint16_t aging;
uint16_t dont_cache_flag;
uint16_t handle_is_fd;
/* memory interface */
const void *data;
/* common interface */
size_t offset; /* file offset */
size_t nested_offset; /* buffer offset for nested scan*/
size_t real_len; /* amount of data mapped from file, starting at offset */
size_t len; /* length of data accessible via current fmap */
/* real_len = nested_offset + len
* file_offset = offset + nested_offset + need_offset
* maximum offset, length accessible via fmap API: len
* offset in cached buffer: nested_offset + need_offset
*
* This allows scanning a portion of an already mapped file without dumping
* to disk and remapping (for uncompressed archives for example) */
/* vtable for implementation */
void (*unmap)(fmap_t *);
const void *(*need)(fmap_t *, size_t at, size_t len, int lock);
const void *(*need_offstr)(fmap_t *, size_t at, size_t len_hint);
const void *(*gets)(fmap_t *, char *dst, size_t *at, size_t max_len);
void (*unneed_off)(fmap_t *, size_t at, size_t len);
#ifdef _WIN32
HANDLE fh;
HANDLE mh;
#endif
unsigned char maphash[16];
uint64_t *bitmap;
char *name;
};ファイルのマッピング処理
今回の clamdscan 要求の場合、スキャン対象のファイルは fmapcheckempty 関数によって fmap_t 構造のメモリにマッピングされます。
参考:clamav/libclamav/fmap.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
fmap_t *fmap_check_empty(int fd, off_t offset, size_t len, int *empty, const char *name)
{
STATBUF st;
fmap_t *m = NULL;
*empty = 0;
if (FSTAT(fd, &st)) {
cli_warnmsg("fmap: fstat failed\n");
return NULL;
}
if (!len) len = st.st_size - offset; /* bound checked later */
if (!len) {
cli_dbgmsg("fmap: attempted void mapping\n");
*empty = 1;
return NULL;
}
if (!CLI_ISCONTAINED(0, st.st_size, offset, len)) {
cli_warnmsg("fmap: attempted oof mapping\n");
return NULL;
}
m = cl_fmap_open_handle((void *)(ssize_t)fd, offset, len, pread_cb, 1);
if (!m)
return NULL;
m->mtime = st.st_mtime;
if (NULL != name) {
m->name = cli_strdup(name);
if (NULL == m->name) {
funmap(m);
return NULL;
}
}
return m;
}この関数ではまず始めに fstat により受け取ったファイルディスクリプタの状態を STATBUF 構造体(stat もしくは stat64)の変数 st に保存します。
STATBUF st;
fmap_t *m = NULL;
*empty = 0;
if (FSTAT(fd, &st)) {
cli_warnmsg("fmap: fstat failed\n");
return NULL;
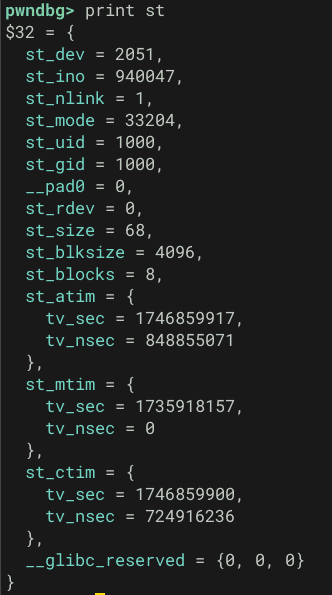
}実際に今回スキャン対象となる eicar.com の場合、fstat により st には以下の情報が書き込まれました。
これらの情報は stat eicar.com と stat コマンドを使用した結果とも一致しており、正しく stat 情報を取得できていることがわかります。
次にファイルのマッピング範囲の検証を行った上で、clfmapopen_handle 関数にファイルディスクリプタなどの情報をパスして実行します。
clfmapopenhandle 関数の中では、calloc によるメモリ割り当てを行う clicalloc 関数で割り当てた fmap_t 構造体のメモリ領域 m にファイルの情報やいくつかのコールバックへのポインタを割り当てます。
m->handle = handle;
m->pread_cb = pread_cb;
m->aging = use_aging;
m->offset = offset;
m->nested_offset = 0;
m->len = len; /* m->nested_offset + m->len = m->real_len */
m->real_len = len;
m->pages = pages;
m->pgsz = pgsz;
m->paged = 0;
m->dont_cache_flag = 0;
m->unmap = unmap_handle;
m->need = handle_need;
m->need_offstr = handle_need_offstr;
m->gets = handle_gets;
m->unneed_off = handle_unneed_off;
m->handle_is_fd = 1;
/* Calculate the fmap hash to be used by the FP check later */
if (CL_SUCCESS != fmap_get_MD5(hash, m)) {
cli_warnmsg("fmap: failed to get MD5\n");
goto done;
}
memcpy(m->maphash, hash, 16);また、fmapgetMD5 関数では割り当てた fmap_t 構造体を使用して MD5 ハッシュの計算を行います。
この処理の実行後、fmap_t 構造体には eicar.com の MD5 ハッシュである 44d88612fea8a8f36de82e1278abb02f が正しく書き込まれていることを確認できます。
さらに、fmapgetMD5 関数の中では fmapneedoffonce 関数により呼び出される m->need (handleneed) により、読み取られたファイルのデータが m->data に保存されていることも確認できます。
scanner の処理を追う
ここまでで、clamdscan からのスキャン要求をトリガーとして実行された clscandesccallback 内で、fmap 関数からコールされた fmapcheckempty 関数によりスキャン対象のファイルが fmap_t 構造でメモリにマッピングされました。
続けて、このマッピングされたファイル情報を引数として scancommon 関数が clscandesc_callback 関数から呼び出されます。
/**
* @brief The main function to initiate a scan of an fmap.
*
* @param map File map.
* @param filepath (optional, recommended) filepath of the open file descriptor or file map.
* @param[out] virname Will be set to a statically allocated (i.e. needs not be freed) signature name if the scan matches against a signature.
* @param[out] scanned The number of bytes scanned.
* @param engine The scanning engine.
* @param scanoptions Scanning options.
* @param[inout] context An opaque context structure allowing the caller to record details about the sample being scanned.
* @return int CL_CLEAN, CL_VIRUS, or an error code if an error occured during the scan.
*/
static cl_error_t scan_common(cl_fmap_t *map, const char *filepath, const char **virname, unsigned long int *scanned, const struct cl_engine *engine, struct cl_scan_options *scanoptions, void *context)参考:clamav/libclamav/scanners.c at main · Cisco-Talos/clamav
scan_common 関数の引数
scancommon 関数呼び出し時にパスされる引数のうち、第 1 引数の `clfmap_t *map` には前項までに確認したメモリにマッピングされた fmap 構造体が含まれます。
第 2 引数の filepath にはスキャン対象のファイルの完全パス(/home/kash1064/Downloads/eicar.com ) が保存されています。
さらに、第 5 引数の const struct cl_engine *engine では、スキャンに使用する cl_engine 構造体の構成情報が含まれます。
この構造体は以下の通り定義されています。
参考:clamav/libclamav/others.h at main · Cisco-Talos/clamav
struct cl_engine {
uint32_t refcount; /* reference counter */
uint32_t sdb;
uint32_t dboptions;
uint32_t dbversion[2];
uint32_t ac_only;
uint32_t ac_mindepth;
uint32_t ac_maxdepth;
char *tmpdir;
uint32_t keeptmp;
uint64_t engine_options;
/* Limits */
uint32_t maxscantime; /* Time limit (in milliseconds) */
uint64_t maxscansize; /* during the scanning of archives this size
* will never be exceeded
*/
uint64_t maxfilesize; /* compressed files will only be decompressed
* and scanned up to this size
*/
uint32_t maxreclevel; /* maximum recursion level for archives */
uint32_t maxfiles; /* maximum number of files to be scanned
* within a single archive
*/
/* This is for structured data detection. You can set the minimum
* number of occurrences of an CC# or SSN before the system will
* generate a notification.
*/
uint32_t min_cc_count;
uint32_t min_ssn_count;
/* Roots table */
struct cli_matcher **root;
/* hash matcher for standard MD5 sigs */
struct cli_matcher *hm_hdb;
/* hash matcher for MD5 sigs for PE sections */
struct cli_matcher *hm_mdb;
/* hash matcher for MD5 sigs for PE import tables */
struct cli_matcher *hm_imp;
/* hash matcher for allow list db */
struct cli_matcher *hm_fp;
/* Container metadata */
struct cli_cdb *cdb;
/* Phishing .pdb and .wdb databases*/
struct regex_matcher *allow_list_matcher;
struct regex_matcher *domain_list_matcher;
struct phishcheck *phishcheck;
/* Dynamic configuration */
struct cli_dconf *dconf;
/* Filetype definitions */
struct cli_ftype *ftypes;
struct cli_ftype *ptypes;
/* Container password storage */
struct cli_pwdb **pwdbs;
/* Pre-loading test matcher
* Test for presence before using; cleared on engine compile.
*/
struct cli_matcher *test_root;
/* Ignored signatures */
struct cli_matcher *ignored;
/* PUA categories (to be included or excluded) */
char *pua_cats;
/* Icon reference storage */
struct icon_matcher *iconcheck;
/* Negative cache storage */
struct CACHE *cache;
/* Database information from .info files */
struct cli_dbinfo *dbinfo;
/* Signature counting, for progress callbacks */
size_t num_total_signatures;
/* Used for memory pools */
mpool_t *mempool;
/* crtmgr stuff */
crtmgr cmgr;
/* Callback(s) */
clcb_pre_cache cb_pre_cache;
clcb_pre_scan cb_pre_scan;
clcb_post_scan cb_post_scan;
clcb_virus_found cb_virus_found;
clcb_sigload cb_sigload;
void *cb_sigload_ctx;
clcb_hash cb_hash;
clcb_meta cb_meta;
clcb_file_props cb_file_props;
clcb_progress cb_sigload_progress;
void *cb_sigload_progress_ctx;
clcb_progress cb_engine_compile_progress;
void *cb_engine_compile_progress_ctx;
clcb_progress cb_engine_free_progress;
void *cb_engine_free_progress_ctx;
/* Used for bytecode */
struct cli_all_bc bcs;
unsigned *hooks[_BC_LAST_HOOK - _BC_START_HOOKS];
unsigned hooks_cnt[_BC_LAST_HOOK - _BC_START_HOOKS];
unsigned hook_lsig_ids;
enum bytecode_security bytecode_security;
uint32_t bytecode_timeout;
enum bytecode_mode bytecode_mode;
/* Engine max settings */
uint64_t maxembeddedpe; /* max size to scan MSEXE for PE */
uint64_t maxhtmlnormalize; /* max size to normalize HTML */
uint64_t maxhtmlnotags; /* max size for scanning normalized HTML */
uint64_t maxscriptnormalize; /* max size to normalize scripts */
uint64_t maxziptypercg; /* max size to re-do zip filetype */
/* Statistics/intelligence gathering */
void *stats_data;
clcb_stats_add_sample cb_stats_add_sample;
clcb_stats_remove_sample cb_stats_remove_sample;
clcb_stats_decrement_count cb_stats_decrement_count;
clcb_stats_submit cb_stats_submit;
clcb_stats_flush cb_stats_flush;
clcb_stats_get_num cb_stats_get_num;
clcb_stats_get_size cb_stats_get_size;
clcb_stats_get_hostid cb_stats_get_hostid;
/* Raw disk image max settings */
uint32_t maxpartitions; /* max number of partitions to scan in a disk image */
/* Engine max settings */
uint32_t maxiconspe; /* max number of icons to scan for PE */
uint32_t maxrechwp3; /* max recursive calls for HWP3 parsing */
/* PCRE matching limitations */
uint64_t pcre_match_limit;
uint64_t pcre_recmatch_limit;
uint64_t pcre_max_filesize;
#ifdef HAVE_YARA
/* YARA */
struct _yara_global *yara_global;
#endif
};第 6 引数では clscanoptions 構造体によりスキャンオプションが指定されます。
/*** scan options ***/
struct cl_scan_options {
uint32_t general;
uint32_t parse;
uint32_t heuristic;
uint32_t mail;
uint32_t dev;
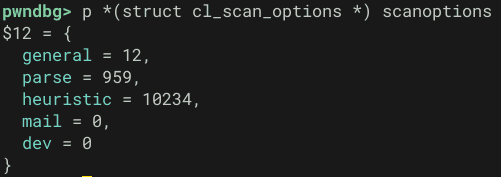
};今回の clamdscan 呼び出し時には以下のオプションが指定されていました。
scancommon 関数が受け取ったこれらの引数は、この後初期化された clictx 構造体の変数 ctx のメンバとして保存されます。
memset(&ctx, '\0', sizeof(cli_ctx));
ctx.engine = engine;
ctx.virname = virname;
ctx.scanned = scanned;
ctx.options = malloc(sizeof(struct cl_scan_options));
memcpy(ctx.options, scanoptions, sizeof(struct cl_scan_options));
ctx.found_possibly_unwanted = 0;
ctx.containers = cli_calloc(sizeof(cli_ctx_container), ctx.engine->maxreclevel + 2);
if (!ctx.containers) {
rc = CL_EMEM;
goto done;
}
cli_set_container(&ctx, CL_TYPE_ANY, 0);
ctx.dconf = (struct cli_dconf *)engine->dconf;
ctx.cb_ctx = context;
fmap_head = cli_calloc(sizeof(fmap_t *), ctx.engine->maxreclevel + 3);
if (!fmap_head) {
rc = CL_EMEM;
goto done;
}
if (!(ctx.hook_lsig_matches = cli_bitset_init())) {
rc = CL_EMEM;
goto done;
}
/*
* The first fmap in ctx.fmap must be NULL so we can fmap-- while not NULL.
* But we need an fmap to be set so we can append viruses or report the
* fmap's file descriptor in the virus found callback (like for deferred
* low-seveerity alerts).
*/
ctx.fmap = fmap_head + 1;
*ctx.fmap = map;この構造体は以下の通り定義されており、スキャン対象のファイルパスやその他の様々なステータス情報を含みます。
この構造体は最終的に cli_magic_scan(&ctx, CL_TYPE_ANY); にて、scancommon 関数から実際にスキャンを行う climagic_scan 関数に渡されます。
/* internal clamav context */
typedef struct cli_ctx_tag {
char *target_filepath; /**< (optional) The filepath of the original scan target */
const char *sub_filepath; /**< (optional) The filepath of the current file being parsed. May be a temp file. */
char *sub_tmpdir; /**< The directory to store tmp files at this recursion depth. */
const char **virname;
unsigned int num_viruses;
unsigned long int *scanned;
const struct cli_matcher *root;
const struct cl_engine *engine;
unsigned long scansize;
struct cl_scan_options *options;
unsigned int recursion;
unsigned int scannedfiles;
unsigned int found_possibly_unwanted;
unsigned int corrupted_input;
unsigned int img_validate;
cli_ctx_container *containers; /* set container type after recurse */
unsigned char handlertype_hash[16];
struct cli_dconf *dconf;
fmap_t **fmap; /* pointer to current fmap in an allocated array, incremented with recursion depth */
bitset_t *hook_lsig_matches;
void *cb_ctx;
cli_events_t *perf;
#ifdef HAVE__INTERNAL__SHA_COLLECT
int sha_collect;
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_JSON
struct json_object *properties;
struct json_object *wrkproperty;
#endif
struct timeval time_limit;
int limit_exceeded;
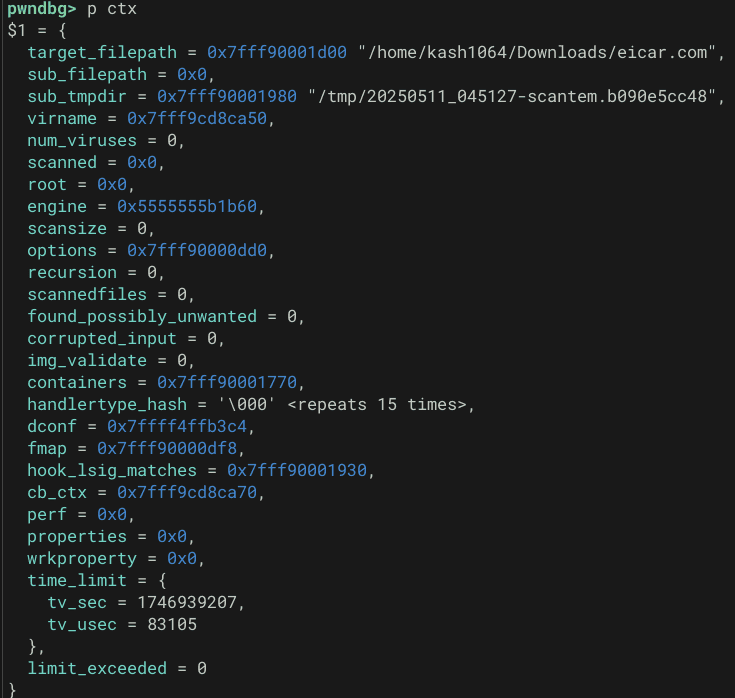
} cli_ctx;climagicscan 関数呼び出し時の ctx をダンプしてみると、以下のような情報が含まれていました。
ファイルタイプの特定
コンテキスト情報が climagicscan 関数に渡された後、いくつかのチェックの後以下のコードが実行されます。
ここでは、clideterminefmaptype 関数と cliftname 関数によりファイルタイプの特定が行われます。
hash = (*ctx->fmap)->maphash;
hashed_size = (*ctx->fmap)->len;
old_hook_lsig_matches = ctx->hook_lsig_matches;
if (type == CL_TYPE_PART_ANY) {
typercg = 0;
}
/*
* Perform file typing from the start of the file.
*/
perf_start(ctx, PERFT_FT);
if ((type == CL_TYPE_ANY) || type == CL_TYPE_PART_ANY) {
type = cli_determine_fmap_type(*ctx->fmap, ctx->engine, type);
}
perf_stop(ctx, PERFT_FT);
if (type == CL_TYPE_ERROR) {
cli_dbgmsg("cli_magic_scan: cli_determine_fmap_type returned CL_TYPE_ERROR\n");
ret = CL_EREAD;
cli_dbgmsg("cli_magic_scan: returning %d %s (no post, no cache)\n", ret, __AT__);
goto early_ret;
}
filetype = cli_ftname(type);ファイルタイプの一覧は libclamav/filetypes.h で定義されており、今回の Eicar ファイルの場合は CL_TYPE_TEXT_ASCII と識別されました。
参考:clamav/libclamav/filetypes.h at main · Cisco-Talos/clamav
キャッシュのチェック
ファイルタイプの特定後、climagicscan 関数では dispatchprescancallback 関数によるチェックも行われるものの、この時点では ctx->engine->cb_pre_cache が NULL のため何も行われず、そのまま cache_check 関数によるチェックが行われます。
ここでは、ctx->engine->cache に格納されている cacheset にスキャン対象のファイルの MD5 ハッシュが含まれるかをチェックし、含まれる場合には CL_VIRUS を返します。
/* Hashes a file onto the provided buffer and looks it up the cache.
Returns CL_VIRUS if found, CL_CLEAN if not FIXME or a recoverable error,
and returns CL_EREAD if unrecoverable */
cl_error_t cache_check(unsigned char *hash, cli_ctx *ctx)
{
fmap_t *map;
int ret;
if (!ctx || !ctx->engine || !ctx->engine->cache)
return CL_VIRUS;
if (ctx->engine->engine_options & ENGINE_OPTIONS_DISABLE_CACHE) {
cli_dbgmsg("cache_check: Caching disabled. Returning CL_VIRUS.\n");
return CL_VIRUS;
}
map = *ctx->fmap;
ret = cache_lookup_hash(hash, map->len, ctx->engine->cache, ctx->recursion);
cli_dbgmsg("cache_check: %02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x is %s\n", hash[0], hash[1], hash[2], hash[3], hash[4], hash[5], hash[6], hash[7], hash[8], hash[9], hash[10], hash[11], hash[12], hash[13], hash[14], hash[15], (ret == CL_VIRUS) ? "negative" : "positive");
return ret;
}今回は Eicar のハッシュがエンジンの cacheset に登録されていたため、まずここでウイルスとして検知されているようでした。
※ cachecheck 関数ではエンジンや cacheset が NULL の場合にもとりあえず CLVIRUS を返して先のスキャンに進むため、必ずしもこの関数が CL_VIRUS を返すとファイルがウイルスとして検出されるわけではないようです。
if (!ctx || !ctx->engine || !ctx->engine->cache)
return CL_VIRUS;キャッシュチェック後のスキャン動作を追跡する
このままだとスキャン動作を追跡しづらいので、一度 clamd.conf で DisableCache を yes に変更してキャッシュの無効化を行います。
# This option allows you to disable clamd's caching feature.
# Default: no
DisableCache yesこの状態で再度 clamdscan によるスキャン要求を行うと、cachecheck 関数による cacheset の照合は行われず、climagic_scan 関数内で先の処理を進めることになります。
いくつかの操作を行った後、climagicscan 関数はスキャン対象のファイルの種類ごとに用意された様々なスキャン関数を呼び出します。
今回の Eicar ファイルは CL_TYPE_TEXT_ASCII と分類されているので、cli_scan_structured(ctx); によるチェックが行われます。
ctx->recursion++;
perf_nested_start(ctx, PERFT_CONTAINER, PERFT_SCAN);
/* set current level as container AFTER recursing */
cli_set_container(ctx, type, (*ctx->fmap)->len);
switch (type) {
case CL_TYPE_IGNORED:
break;
/* 省略 */
case CL_TYPE_BINARY_DATA:
case CL_TYPE_TEXT_UTF16BE:
if (SCAN_HEURISTICS && (DCONF_OTHER & OTHER_CONF_MYDOOMLOG))
ret = cli_check_mydoom_log(ctx);
break;
case CL_TYPE_TEXT_ASCII:
if (SCAN_HEURISTIC_STRUCTURED && (DCONF_OTHER & OTHER_CONF_DLP))
/* TODO: consider calling this from cli_scanscript() for
* a normalised text
*/
ret = cli_scan_structured(ctx);
break;
default:
break;
}
perf_nested_stop(ctx, PERFT_CONTAINER, PERFT_SCAN);
ctx->recursion--;しかし、この関数は DLP の用途でクレジットカード番号や SSN の番号が含まれるかをチェックするもののようで、今回は無視できそうです。
さらに climagicscan 関数の処理を追跡すると、最終的に scanraw(ctx, type, typercg, &dettype, (ctx->engine->engine_options & ENGINE_OPTIONS_DISABLE_CACHE) ? NULL : hash); によるチェックを行うことがわかりました。
/* CL_TYPE_HTML: raw HTML files are not scanned, unless safety measure activated via DCONF */
if (type != CL_TYPE_IGNORED && (type != CL_TYPE_HTML || !(SCAN_PARSE_HTML) || !(DCONF_DOC & DOC_CONF_HTML_SKIPRAW)) && !ctx->engine->sdb) {
res = scanraw(ctx, type, typercg, &dettype, (ctx->engine->engine_options & ENGINE_OPTIONS_DISABLE_CACHE) ? NULL : hash);
if (res != CL_CLEAN) {
switch (res) {
/* List of scan halts, runtime errors only! */
/* 省略 */
case CL_VIRUS:
ret = res;
if (SCAN_ALLMATCHES)
break;
cli_bitset_free(ctx->hook_lsig_matches);
ctx->hook_lsig_matches = old_hook_lsig_matches;
goto done;
/* 省略 */
}
}
}scanraw 関数は、スキャン対象のファイルをマップした fmap に対して raw scan を実行する関数とのことですので、実際のいわゆるファイルスキャンはこの中で行われていそうです。
/**
* @brief Perform raw scan of current fmap.
*
* @param ctx Current scan context.
* @param type File type
* @param typercg Enable type recognition (file typing scan results).
* If 0, will be a regular ac-mode scan.
* @param[out] dettype If typercg enabled and scan detects HTML or MAIL types,
* will output HTML or MAIL types after performing HTML/MAIL scans
* @param refhash Hash of current fmap
* @return cl_error_t
*/
static cl_error_t scanraw(cli_ctx *ctx, cli_file_t type, uint8_t typercg, cli_file_t *dettype, unsigned char *refhash)しかし、raw scan を実行する scanraw 関数ですが、ここでもスキャン対象のファイルタイプに合わせて様々なスキャン処理が呼び出されており、実際の Eicar の検出は cliscanfmap 関数の中で行われるようです。
perf_start(ctx, PERFT_RAW);
ret = cli_scan_fmap(ctx, type == CL_TYPE_TEXT_ASCII ? CL_TYPE_ANY : type, 0, &ftoffset, acmode, NULL, refhash);
perf_stop(ctx, PERFT_RAW);cliscanfmap 関数内では、ファイルを一定のバッファサイズごとに読み込みシグネチャマッチャーを使用したスキャンを行う方法と、ハッシュベースのスキャンを行う 2 つのチェックを行うようです。
ハッシュベースのスキャンに使用するデータベース(hdb) は ctx->engine->hm_hdb の情報を使用します。
今回使用した Eicar ファイルは、以下の箇所でハッシュベースで検出されました。
hdb = ctx->engine->hm_hdb;
fp = ctx->engine->hm_fp;
/* 省略 */
virname = NULL;
for (hashtype = CLI_HASH_MD5; hashtype < CLI_HASH_AVAIL_TYPES; hashtype++) {
const char *virname_w = NULL;
int found = 0;
/* If no hash, skip to next type */
if (!compute_hash[hashtype])
continue;
/* Do hash scan */
if ((ret = cli_hm_scan(digest[hashtype], map->len, &virname, hdb, hashtype)) == CL_VIRUS) {
found += 1;
}
if (!found || SCAN_ALLMATCHES) {
if ((ret = cli_hm_scan_wild(digest[hashtype], &virname_w, hdb, hashtype)) == CL_VIRUS)
found += 2;
}
/* If found, do immediate hash-only FP check */
if (found && fp) {
for (hashtype2 = CLI_HASH_MD5; hashtype2 < CLI_HASH_AVAIL_TYPES; hashtype2++) {
if (!compute_hash[hashtype2])
continue;
if (cli_hm_scan(digest[hashtype2], map->len, NULL, fp, hashtype2) == CL_VIRUS) {
found = 0;
ret = CL_CLEAN;
break;
} else if (cli_hm_scan_wild(digest[hashtype2], NULL, fp, hashtype2) == CL_VIRUS) {
found = 0;
ret = CL_CLEAN;
break;
}
}
}
/* If matched size-based hash ... */
if (found % 2) {
viruses_found = 1;
ret = cli_append_virus(ctx, virname);
if (!SCAN_ALLMATCHES || ret != CL_CLEAN)
break;
virname = NULL;
}
/* If matched size-agnostic hash ... */
if (found > 1) {
viruses_found = 1;
ret = cli_append_virus(ctx, virname_w);
if (!SCAN_ALLMATCHES || ret != CL_CLEAN)
break;
}
}ハッシュベースのスキャン時には、最終的に hm_scan 関数が使用されます。
この中では、cliszhash 構造体に含まれるハッシュリストがスキャン対象のハッシュと一致するかを hm_cmp 関数を使用してチェックしています。
/* cli_hm_scan will scan only size-specific hashes, if any */
static int hm_scan(const unsigned char *digest, const char **virname, const struct cli_sz_hash *szh, enum CLI_HASH_TYPE type)
{
unsigned int keylen;
size_t l, r;
if (!digest || !szh || !szh->items)
return CL_CLEAN;
keylen = hashlen[type];
l = 0;
r = szh->items - 1;
while (l <= r) {
size_t c = (l + r) / 2;
int res = hm_cmp(digest, &szh->hash_array[keylen * c], keylen);
if (res < 0) {
if (!c)
break;
r = c - 1;
} else if (res > 0)
l = c + 1;
else {
if (virname)
*virname = szh->virusnames[c];
return CL_VIRUS;
}
}
return CL_CLEAN;
}参考:clamav/libclamav/matcher-hash.c at rel/0.104 · kash1064/clamav
この時、hm_cmp 関数は比較対象のハッシュを辞書順の大小結果で返すため、ハッシュリストの検索は二分探索のアルゴリズムを使用して行っています。
また、そもそものハッシュテーブル自体も、事前に clihtu32find 関数でスキャン対象のハッシュの先頭バイトを Key として抽出したものを使用しているため、スキャン対象のテーブル自体も比較的小さくなっています。
このようにして効率的にハッシュベースのスキャンを行うことで Eicar などの既知のウイルスを検出しているようです。
なお、以上の操作で Eicar ファイルの検出を行った後は、同じく clihmscan 関数を使用して fp データベースとの照合を行うようです。
まとめ
思ったよりシンプルな実装でしたが、それでも分岐やジャンプが多くて読むのがしんどかったです。
後半だいぶグダりましたが、とりあえず Eicar 検出に関するスキャン動作を一通り見てみました。